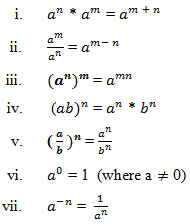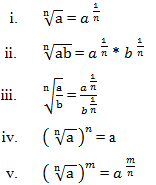Power: -
घातांक, जिन्हें घात भी कहा जाता है, एक संख्या को एक निश्चित संख्या से गुणा करके व्यक्त करने का एक तरीका है।
जब हम कोई संख्या a लिखते हैं, तो वह वास्तव में a1 होती है, जिसे a घात 1 कहा जाता है।
a2 = a*a
a3 = a*a*a
:
:
an = a*a*a*a* . . . n times.
Indices: -
जब एक संख्या (a) को स्वयं "n" से गुणा किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए एक
यहां 'a' को आधार कहा जाता है और 'n' को Power के सूचकांक के रूप में जाना जाता है। मूल रूप से यह एक घातीय अभिव्यक्ति है।
Rules of Power: -
Rules of Indices: -
सूचकांक: - एक गैर ऋणात्मक परिमेय संख्या का कोई भी मूल, जो पाया नहीं जा सकता है या सटीक समाधान प्रदान नहीं करता है। उदाहरण के लिए n
यहां 'a' को radicand कहा जाता है और 'n' को Surd के क्रम के रूप में जाना जाता है। 'n' एक प्राकृत संख्या होनी चाहिए।
नोट: - सभी सर्ड अपरिमेय संख्या होते हैं लेकिन सभी अपरिमेय संख्याएं सर्ड नहीं होती हैं।
Order of the surds:
a) दूसरे कोटि के सर्ड को द्विघात सर्ड के रूप में जाना जाता है।
b) तीसरे क्रम के सर्ड को क्यूबिक सर्ड के रूप में जाना जाता है।
Rules of Surds: -
Type of Surds: -
- Pure Surds:- वे सर्ड जिनका 1 के अलावा कोई गुणनखंड नहीं होता है। उदाहरण के लिए 2√3, 3√7
- Mixed Surds:- वे सर्ड जिनका गुणनखंड 1 से अधिक नहीं होता है। उदाहरण के लिए 27 = 3√3, √50 = 5√2
- Similar Surds:- जब दो सूरों के मूलांक समान हों। उदाहरण के लिए 5√2 और 7√2
- Unlike Surds:- जब मूलांक भिन्न होते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए √2 और 2√5
Formulas/ Patterns Including Short Tricks:
1) Arrangement of surds in either increasing or decreasing order –
First of all, take the LCM of the denominator of the powers and use it to make them same and then solve it.Example: -

2) Calculation on indices/ surds to find the value of any expression –
In such questions, factorize the expression in the smallest possible number then solve the expression using the rules of surds/ indices.Example: -

3) Addition operation on surds –

In such questions, break the x into m (m + 1) form then answer would be (m + 1).
Example: -

4) Subtraction operation on surds –
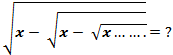
In such questions, factorize the x into m (m + 1) form then ‘m’ would be the answer.
Example: -

5) Multiplication operation on surds –

In such questions, answer would be

Where n = number of time x is repeated.
Example: -

6) Rationalization on surds –
In this process, we convert the denominator of the surds into a rational number. For this we have to multiply both numerator and denominator of the surds with another surd and obtain rational number by applying formula (a + b) * (a – b) = (a2- b2)
Example: -
Find the value of